The public in general tend to believe that email authentication is difficult subject. There is a mixture of acronyms and initialisms. There are often random links to technologies that are clear only for professionals. For sure, there are some main concepts which are not rocket science and most everyone can get them.
Email authentication has become vital as spammers and phishers continue to spread harmful messages through email. Most email servers now use variety of protocols to inspect messages before they reach the recipient . Messages that are not properly authenticated are likely to have deliverability problems and end up undelivered or in the spam folder.
Let’s consider 3 crucial email authentication protocols for everybody to understand.
SPF – Sender Policy Framework
Sender Policy Framework (SPF)- is the first and oldest. SPF allows a sender to check their originality. You can be sure that a letter is authentic if it is printed on official letterhead in your mailbox or it is a certified letter from the post office. By calling the post office you can verify who the sender through a tracking number.
SPF is also similar to approving a return address. You should be skeptical of a letter where the business name didn’t match any businesses listed at the letter’s return address. This kind of control is usually unnecessary for physical mail, but it is useful for email because it’s trivially easy to send a message claiming to be from someone else.
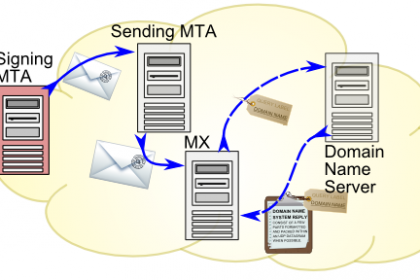
During SPF, a receiving email server can ask the domain that the email claims to be from for a list of IP addresses that are allowed to send email on that domain’s behalf. The email is most likely not original and the SPF check will fail if the domain doesn’t contain the originating server as a valid sender.
DKIM – Domain Keys Identified Mail
Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM)- is a newer and more trustful way to authenticate messages. Before reliable postal infrastructure, letters were certified by a sealing wax embossed with a signet ring belonging to the sender. The hardened wax bonded with the parchment and made it nearly impossible to tamper with the letter without leaving evidence.
The symbol pressed into the wax served as a kind of signature, as only one person would have had access to the signet ring. By inspecting the envelope, the recipient could verify both the authenticity of the sender and that the contents were unaltered.
Another way to ensure the authenticity is a box with a locking drawer and a locking lid. The drawer can only be locked with the sender’s key -private key. The key is freely available, so we can consider it as a public key.
DKIM works like this. The sender has a cryptographic private key that is used to encode the message headlines. The public key is made available on a decentralized public net registry called the DNS or Domain Name System. Any of the servers can retrieve the public key and decrypt the headlines to ensure that the message is valid.
DKIM-authenticated messages are registered mail, kept under lock and key at all times along the delivery way to prevent tampering.
DMARC – Domain Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance
SPF + DKIM = DMARC is the latest authentication tool. It’s a way for senders to inform recipients which authentication methods to check for and what to do if a message supposedly from them does not pass the necessary checks. The user might include marking the message as quarantined and therefore likely to be suspicious or completely rejecting the message.
DMARC also provides a feedback loop so senders can control whether emails that appear to be originating from their domains are in accordance with the policy or not.
A sharp change to a strict DMARC policy would negatively impact many senders, so they continue to allow messages that fail DMARC to be delivered. However, that will be changing soon.
What Email Authentication Means For Senders
You should never send from domains that are not configured to allow your server via DKIM and SPF. If you send emails on behalf of clients, you’ll want to ensure your clients have the correct DNS entries in place to enable this.


